Shape language, a captivating and multifaceted realm of communication, sets the stage for this enthralling narrative. Embark on a journey through time, exploring its origins, evolution, and diverse applications, as we unravel the profound cultural significance embedded within its intricate gestures.
From the enigmatic hand gestures of ancient civilizations to the expressive body language of modern-day interactions, shape language weaves a tapestry of meaning, transcending linguistic barriers and connecting individuals across cultures. Join us as we delve into its captivating world, deciphering the nuances and uncovering the hidden messages conveyed through the dance of shapes.
Historical Context of Shape Language
Shape language, a non-verbal communication method, has a rich history that spans across various cultures and time periods.
The earliest evidence of shape language dates back to ancient Egypt, where hieroglyphs were used to represent objects, ideas, and sounds. In ancient Greece, hand gestures were employed in theater and public speaking to convey emotions and emphasize points.
Origins and Evolution of Shape Language
The development of shape language was influenced by factors such as trade, exploration, and cultural exchange. Merchants and travelers introduced new gestures and symbols into different regions, leading to the evolution of a shared vocabulary of shapes.
In the 18th century, the Abbé de l’Épée developed a system of sign language for the deaf, which incorporated elements of shape language. This system, known as French Sign Language, became the basis for many modern sign languages around the world.
Role of Shape Language in Ancient Communication Systems
Shape language played a significant role in ancient communication systems. It was used in:
- Military signaling: Shapes were used to convey messages across long distances, such as battle formations and troop movements.
- Religious rituals: Shape language was incorporated into religious ceremonies and rituals to symbolize sacred concepts and communicate with the divine.
- Trade and commerce: Merchants used shape language to negotiate prices and communicate with customers from different linguistic backgrounds.
Types and Forms of Shape Language
Shape language encompasses a diverse array of communication methods that utilize the form and movement of the body to convey meaning. These include hand gestures, body language, and sign language.
Hand Gestures
Hand gestures are a ubiquitous form of shape language. They can range from simple pointing and waving to complex, culturally specific gestures. Different hand shapes, orientations, and movements can convey a wide range of meanings, from indicating direction to expressing emotions or conveying specific commands.
Body Language
Body language refers to the use of the entire body to communicate. It includes posture, facial expressions, eye contact, and other physical cues. Body language can reveal a person’s emotions, attitudes, and intentions, even when they are not speaking.
Sign Language
Sign language is a fully developed language that uses hand gestures, facial expressions, and body movements to convey meaning. It is primarily used by deaf and hard-of-hearing individuals, but it can also be used by hearing people as a means of communication.
The cultural and contextual variations in shape language usage are significant. Different cultures have their own unique sets of gestures and body language cues, and the meaning of a particular gesture can vary depending on the context in which it is used.
Applications of Shape Language

Shape language finds applications in various fields, enhancing communication, education, and entertainment. Its versatility allows it to serve diverse purposes, including accessibility for people with disabilities and artistic expression.
Communication
Shape language plays a crucial role in communication, particularly for individuals with disabilities. It provides a non-verbal means of expression, enabling them to convey messages and participate in conversations. For example, sign language, a form of shape language, is widely used by deaf and hard of hearing individuals to communicate.
Education
In the realm of education, shape language serves as a valuable tool for teaching and learning. It helps students visualize complex concepts, making them easier to understand and remember. For instance, teachers may use hand gestures to demonstrate mathematical equations or geometric shapes, enhancing student comprehension.
Entertainment, Shape language
Shape language is an integral part of artistic expressions, such as dance and theater. In dance, performers use their bodies to create shapes and movements that convey emotions and tell stories. Similarly, in theater, actors employ gestures and body language to enhance character portrayal and convey messages to the audience.
Interpretation and Analysis of Shape Language
Interpreting and analyzing shape language cues require careful observation and consideration of the context in which they occur. Understanding the meaning behind shapes involves deciphering their forms, orientations, and interactions with other nonverbal cues.
Guidelines for Interpretation
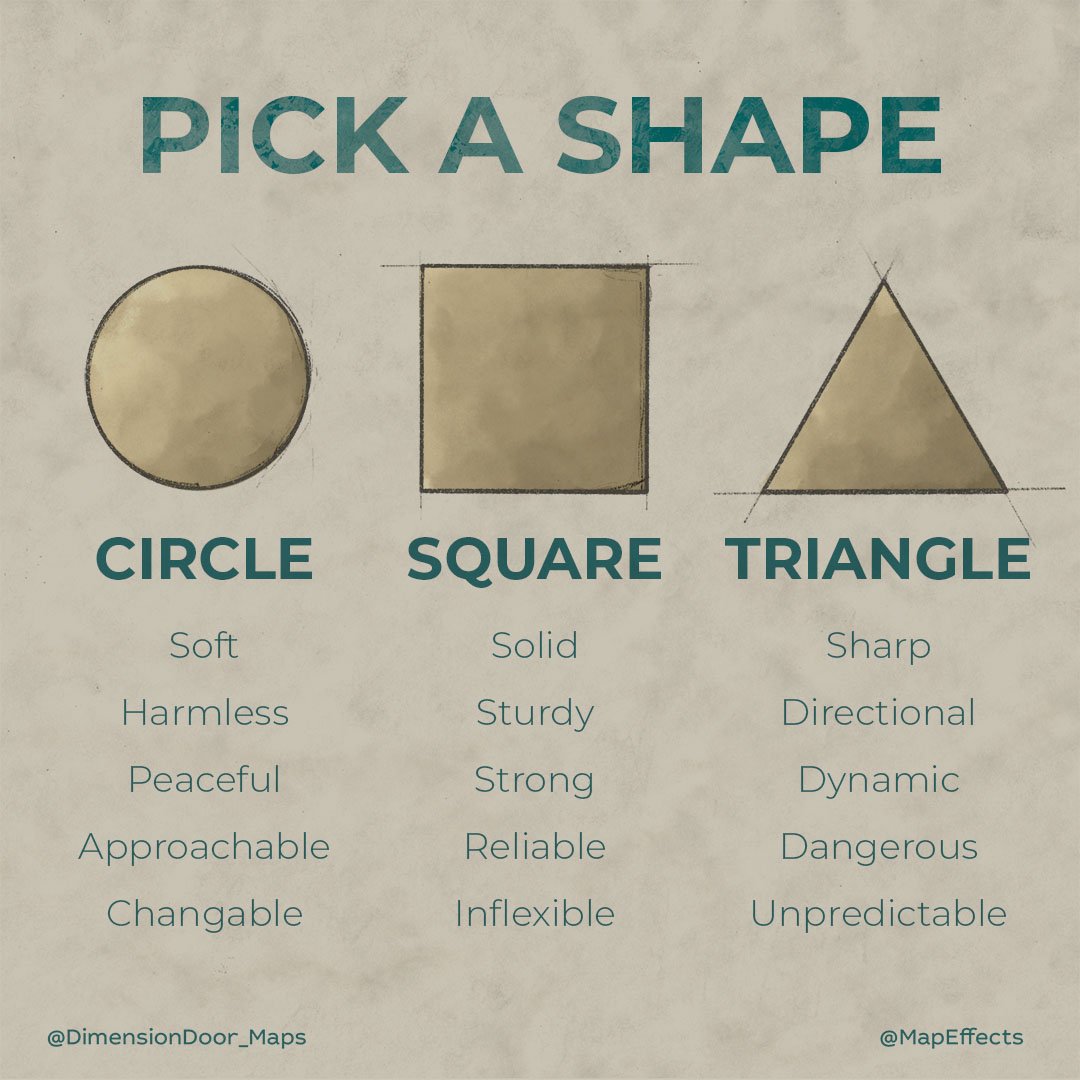
- Observe the overall shape:Identify the dominant shape (e.g., circle, square, triangle) and its variations.
- Pay attention to orientations:Shapes can be upright, tilted, or inverted, conveying different meanings.
- Consider intersections and overlaps:Overlapping or intersecting shapes can indicate connections, conflicts, or transitions.
- Look for consistency and repetition:Repeated shapes or patterns often emphasize or reinforce a particular message.
Importance of Context and Nonverbal Cues
Shape language interpretation is greatly influenced by the context in which it occurs. Factors such as the cultural background, social setting, and the speaker’s intentions all impact the meaning of shapes.
Nonverbal cues, such as facial expressions, gestures, and body language, provide additional insights into the message being conveyed. Combining shape language analysis with other nonverbal cues enhances the accuracy and depth of interpretation.
Challenges and Limitations
Interpreting shape language poses certain challenges:
- Subjectivity:The interpretation of shapes can be subjective, as different individuals may assign different meanings to the same shapes.
- Contextual dependence:The meaning of shapes is highly dependent on the context, making it challenging to generalize interpretations across different situations.
- Cultural variations:Shape language meanings can vary significantly across cultures, requiring careful consideration of the cultural context.
Cultural and Social Significance of Shape Language
Shape language holds profound cultural and social significance across diverse societies, serving as a mirror of their norms, values, and beliefs. It provides insights into the collective psyche and shared experiences of a group, offering a window into their cultural identity.
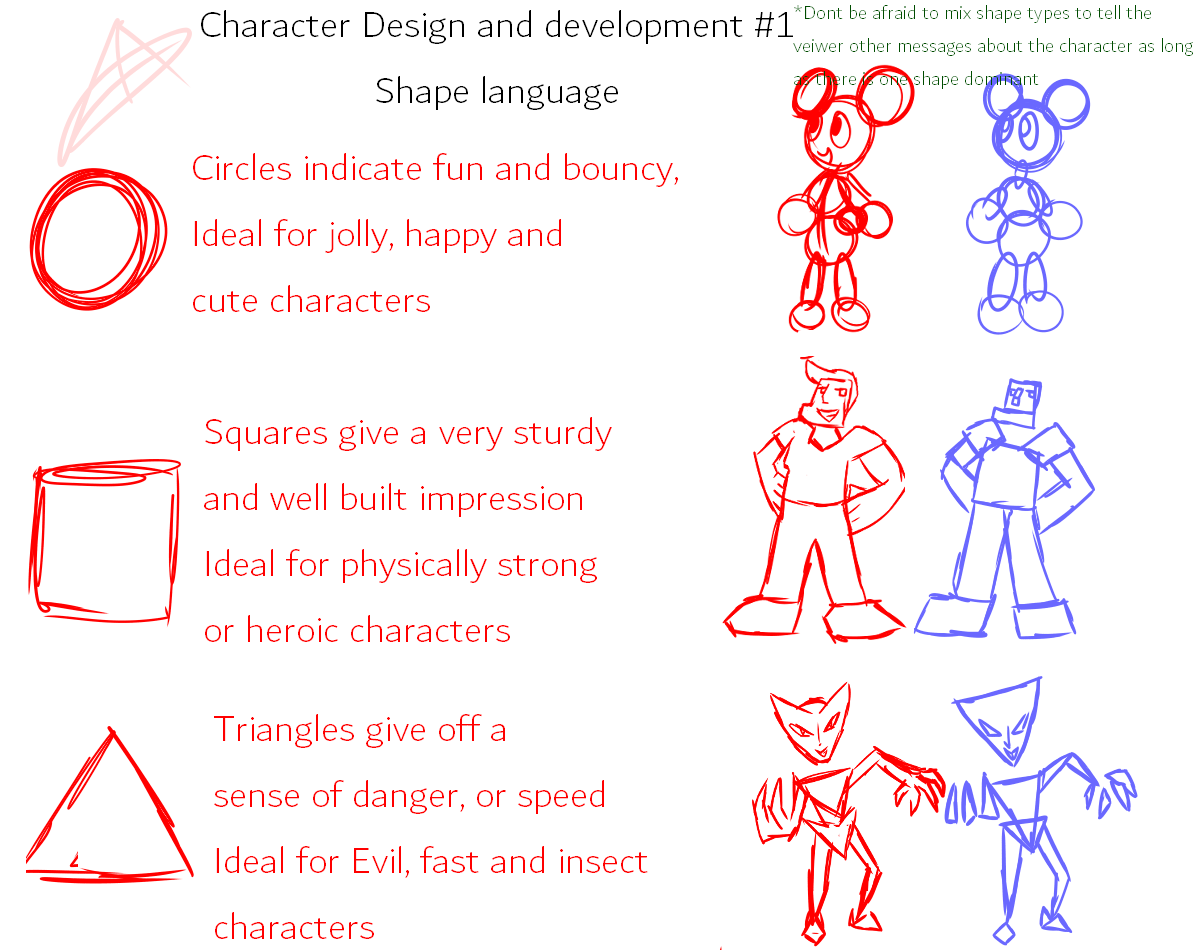
The use of shapes in art, architecture, and everyday objects reflects the cultural values and beliefs of a society. For example, the circle, a symbol of unity and wholeness, is prevalent in many cultures, representing concepts such as the sun, the moon, and the divine.
In contrast, the triangle, with its three points, may symbolize the trinity, the three stages of life, or the balance between heaven, earth, and the underworld.
Impact of Social Factors
Social factors play a significant role in the development and use of shape language. The status, gender, and age of an individual can influence their use of shapes, as can the context in which they are used. For example, in some cultures, certain shapes may be reserved for royalty or religious figures, while others may be considered appropriate for everyday use.
Closing Summary
In conclusion, shape language stands as a testament to the power of nonverbal communication, shaping our interactions, enriching our understanding, and bridging cultural divides. Its profound impact on human expression, from ancient rituals to contemporary art forms, underscores its enduring significance.
As we continue to explore the depths of this captivating language, we unlock a deeper appreciation for the multifaceted ways in which we communicate and connect.
FAQ Section: Shape Language
What is the historical significance of shape language?
Shape language has a rich history, dating back to ancient times. It was used as a primary means of communication before the advent of spoken language and has played a vital role in cultural and social interactions throughout human history.
How does shape language vary across cultures?
Shape language can vary significantly across cultures, as different gestures and body movements can convey different meanings in different contexts. It is important to be aware of these cultural variations to avoid misunderstandings.
What are the applications of shape language in modern society?
Shape language has a wide range of applications in modern society, including communication for people with disabilities, artistic expression in dance and theater, and as a tool for enhancing communication in fields such as education and business.