Embark on a captivating journey into the fascinating world of canine communication with our Dog Body Language Chart. This comprehensive guide empowers you to decipher the intricate signals your furry companion sends, fostering a deeper understanding and stronger bond.
Our chart encompasses a wide range of body parts, including the tail, ears, and eyes, meticulously organized into categories of friendly, aggressive, and submissive behaviors. With real-life examples and expert insights, you’ll gain invaluable knowledge to interpret your dog’s body language effectively.
Dog Body Language Overview: Dog Body Language Chart
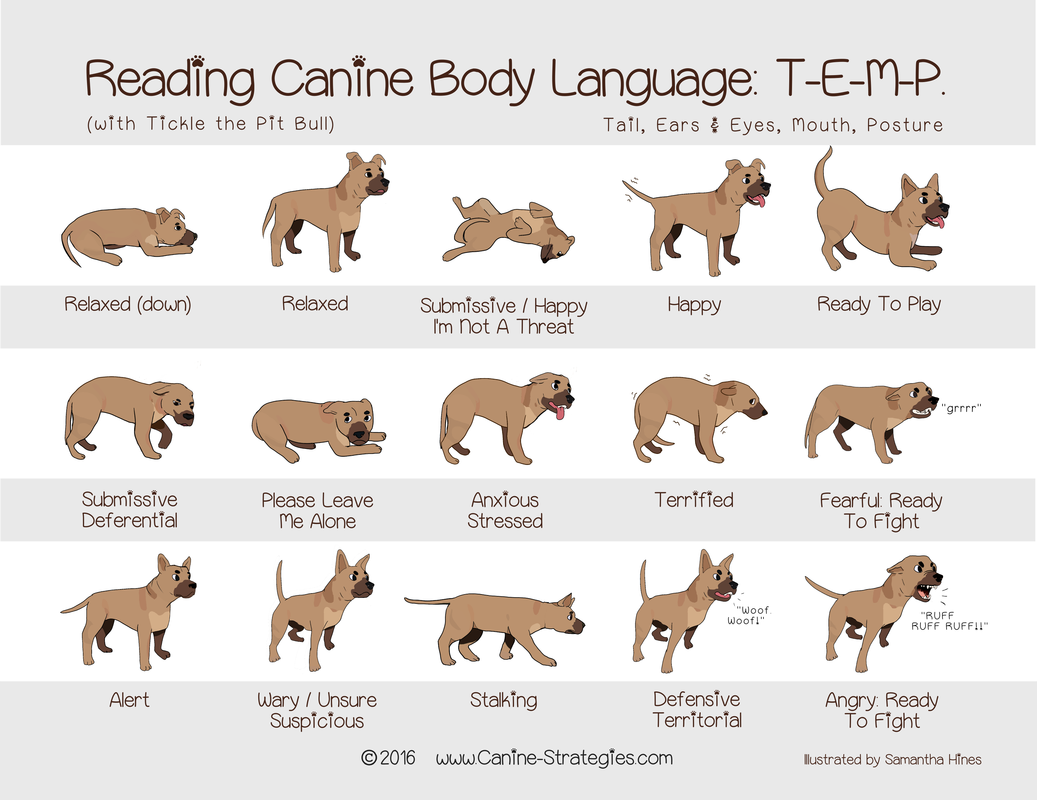
Understanding dog body language is crucial for effective communication and building a harmonious relationship with your canine companion. Dogs communicate primarily through their body language, conveying a wide range of emotions, intentions, and needs. By observing and interpreting these subtle cues, you can gain valuable insights into your dog’s mental and physical well-being, fostering a deeper bond and enhancing your ability to respond appropriately to their needs.
Common dog body language signals include:
- Tail wagging:A wagging tail is often associated with happiness, but the direction and speed of the wag can indicate different emotions. A slow, relaxed wag to the right suggests contentment, while a fast, high wag to the left may indicate excitement or aggression.
- Ears:Dog ears are highly expressive. Forward-facing ears indicate alertness or curiosity, while ears pulled back or flattened against the head can signal fear or submission.
- Eyes:Dogs communicate through eye contact. Direct eye contact can be a sign of dominance or aggression, while averted eyes may indicate submission or fear.
- Body posture:A dog’s body posture can convey a range of emotions. A relaxed, upright posture with a wagging tail suggests happiness, while a hunched posture with tucked tail may indicate fear or anxiety.
Tips for Observing and Interpreting Dog Body Language
To effectively observe and interpret dog body language, follow these tips:
- Pay attention to the context:Consider the situation and environment when interpreting body language. A wagging tail in a playful setting may indicate excitement, while the same behavior in a tense situation may suggest aggression.
- Observe multiple cues:Don’t rely on a single body language cue. Look for a combination of signals to determine the dog’s overall emotional state.
- Be patient:Building trust and establishing a rapport with a dog takes time. Allow your dog to feel comfortable in your presence before attempting to interpret their body language.
- Seek professional help:If you’re unsure about a dog’s body language, consult with a veterinarian or certified dog trainer for guidance.
Dog Body Language Chart
A comprehensive dog body language chart provides an organized reference for interpreting canine behavior. It categorizes various body parts and their associated signals, aiding in understanding a dog’s emotional state and intentions.
The chart is structured into sections, each focusing on a specific body part and its potential meanings. Categories are established to classify the signals into distinct behavioral groups, such as friendly, aggressive, or submissive.
Tail
- Wagging:Can indicate excitement, friendliness, or playfulness. The height and speed of the wag can provide additional context.
- Tucked:Often signifies fear, submission, or anxiety. May be accompanied by other submissive body language cues.
- Raised:Can be a sign of aggression, dominance, or alertness. Combined with other aggressive cues, it may indicate an imminent threat.
Examples of Dog Body Language

To further illustrate the significance of dog body language, let’s explore real-life examples that demonstrate how dogs communicate their emotions and intentions.
By understanding these examples, we can develop a deeper understanding of our canine companions and enhance our interactions with them.
Positive Body Language
When a dog is feeling happy and comfortable, they may exhibit the following body language cues:
- Relaxed body posture:The dog’s body is loose and relaxed, with no signs of tension or stiffness.
- Tail wagging:A slow, relaxed tail wag indicates contentment and friendliness.
- Open mouth with panting:This is a sign of happiness and relaxation, especially in hot weather.
- Ears forward and relaxed:The dog is alert and engaged with its surroundings.
Negative Body Language
On the other hand, when a dog is feeling stressed, anxious, or threatened, they may display the following body language cues:
- Tense body posture:The dog’s body is rigid and tense, with muscles tightened.
- Tail tucked between legs:This is a classic sign of fear or submission.
- Growling:A low, rumbling sound that indicates aggression or warning.
- Ears back and flattened:The dog is feeling fearful or threatened.
How to Use the Dog Body Language Chart
The dog body language chart is a valuable tool for understanding your dog’s behavior. By learning to identify and interpret specific body language signals, you can gain insights into your dog’s emotional state, intentions, and needs.
To use the chart effectively, start by observing your dog in different situations. Pay attention to their body posture, facial expressions, tail movements, and vocalizations. Match what you observe to the corresponding signals on the chart. Consider the context of the situation and your dog’s overall demeanor to interpret the signals accurately.
Tips for Applying the Chart in Real-Life Scenarios
- Use the chart as a reference, not a definitive guide. Body language signals can vary between individual dogs, and context is crucial for accurate interpretation.
- Combine body language observations with other cues, such as your dog’s behavior and vocalizations, to get a comprehensive understanding of their state.
- Observe your dog over time to learn their unique body language patterns. This will help you recognize subtle changes that may indicate a change in their mood or intentions.
Dog Body Language in Specific Situations
Dog body language can vary significantly depending on the situation. For example, a dog’s body language in a social interaction with another dog may be very different from its body language in a training session or a veterinary appointment. It is important to consider the context of the situation when interpreting dog body language.
Here are some examples of how dog body language can vary in different situations:
Social Interactions, Dog body language chart
- In a social interaction with another dog, a dog may display body language that indicates friendliness, such as a wagging tail, relaxed ears, and a playful stance.
- If a dog feels threatened by another dog, it may display body language that indicates aggression, such as a raised hackles, bared teeth, and a stiff posture.
Training Sessions
- In a training session, a dog may display body language that indicates attentiveness, such as making eye contact with the trainer and following commands.
- If a dog is confused or frustrated during a training session, it may display body language that indicates stress, such as pacing, yawning, or licking its lips.
Veterinary Appointments
- At a veterinary appointment, a dog may display body language that indicates fear or anxiety, such as hiding, trembling, or avoiding eye contact.
- If a dog is feeling pain, it may display body language that indicates discomfort, such as licking or chewing at a specific area of its body.
It is important to adjust the interpretation of dog body language based on the context of the situation. By considering the context, you can better understand what your dog is trying to communicate.
Advanced Dog Body Language Analysis
Advanced dog body language analysis involves a deeper understanding of canine communication and the ability to interpret complex and subtle cues. It goes beyond the basics of body language and delves into the nuances of canine behavior.
To effectively analyze dog body language, it’s crucial to consider multiple signals simultaneously. Dogs communicate through a combination of postures, facial expressions, tail movements, and vocalizations. By observing these cues in conjunction, you can gain a more comprehensive understanding of their emotional state and intentions.
Subtle and Complex Body Language Cues
Subtle and complex body language cues require a keen eye and a thorough understanding of canine behavior. These cues can include:
- Ear position:Ears that are slightly forward and alert indicate interest or attention. Ears that are pinned back or held flat against the head may signify fear or submission.
- Tail wagging:While a wagging tail is often associated with happiness, the speed, amplitude, and direction of the wag can convey different messages. A slow, low wag may indicate uncertainty, while a fast, high wag may indicate excitement.
- Facial expressions:Dogs have a wide range of facial expressions that can convey emotions such as joy, fear, anger, and surprise. The shape of the mouth, the position of the eyebrows, and the tension in the face can all provide valuable insights into a dog’s state of mind.
Common Misinterpretations of Dog Body Language

Understanding dog body language is essential for fostering effective communication and building a strong bond with your canine companion. However, certain misconceptions and misinterpretations can arise, leading to incorrect assumptions about a dog’s emotional state and intentions.
Misinterpretation of Tail Wagging
A common misconception is that all tail wags indicate happiness or excitement. While it’s true that dogs do wag their tails when they’re happy, they can also wag their tails when they’re anxious, nervous, or even aggressive. The speed, amplitude, and position of the tail wag provide crucial context for understanding the dog’s mood.
Mistaking Growling for Aggression
Growling is often perceived as a sign of aggression, but it can also be a form of communication. Dogs growl to warn others to stay away, to protect their territory, or to express discomfort. It’s important to observe the dog’s overall body language and context to determine the true intent behind the growling.
Ignoring Subtle Cues
Many people tend to focus on obvious body language cues, such as barking or tail wagging, while ignoring more subtle signals. However, subtle cues, such as ear position, eye contact, and body posture, can provide valuable insights into a dog’s emotional state.
By paying attention to these subtle cues, you can gain a more comprehensive understanding of your dog’s behavior.
Tips for Avoiding Misinterpretations
- Observe the dog’s entire body language, not just one or two cues.
- Consider the context and the dog’s past experiences.
- Avoid anthropomorphizing the dog’s behavior and projecting human emotions onto it.
- Educate yourself about dog body language through books, articles, or workshops.
- Consult with a veterinarian or certified dog trainer if you’re unsure about a dog’s body language.
Cultural Differences in Dog Body Language
Dog body language can vary significantly across different cultures, as cultural factors influence how dogs are trained, socialized, and perceived. Understanding these differences is crucial for effective communication and preventing misunderstandings between humans and dogs.
Influence of Culture on Dog Body Language
- Training and Socialization:Cultural norms and practices regarding dog training and socialization shape dogs’ body language. For example, dogs trained using positive reinforcement may exhibit more relaxed and playful body language, while dogs trained using aversive methods may display more submissive or fearful body language.
- Cultural Perception:Cultural beliefs and attitudes towards dogs influence how people interpret their body language. In some cultures, dogs are seen as loyal companions, while in others, they may be viewed as a nuisance or a threat. These perceptions can affect how humans interact with dogs and how dogs respond to them.
Body Language Variations Across Breeds and Regions
- Breed Differences:Different dog breeds have been selectively bred for specific purposes, which has influenced their body language. For example, herding breeds may display more active and alert body language, while toy breeds may exhibit more playful and submissive body language.
- Regional Differences:Cultural differences can also lead to variations in dog body language within the same breed. For example, dogs in urban areas may be more accustomed to crowds and noise, and may exhibit less fearful body language in these environments compared to dogs in rural areas.
Guidelines for Understanding Cultural Differences in Dog Body Language
- Observe and Contextualize:When interacting with dogs from different cultures, it is important to observe their body language in context. Consider the cultural background of the dog and the environment in which you are interacting.
- Seek Local Guidance:If you are unsure about how to interpret a dog’s body language, seek guidance from a local dog trainer or veterinarian who is familiar with the cultural norms of the area.
- Be Patient and Respectful:Dogs may take time to adjust to new cultural environments. Be patient and respectful of their body language, and allow them to acclimate at their own pace.
Last Word
Unveiling the nuances of dog body language not only enhances communication but also strengthens the bond between you and your canine friend. By embracing this knowledge, you embark on a journey of mutual understanding, creating a harmonious and fulfilling relationship.
Expert Answers
What are some common dog body language signals?
Common signals include a wagging tail (friendliness), pinned-back ears (fear or aggression), and direct eye contact (dominance or challenge).
How can I use the Dog Body Language Chart?
Refer to the chart to identify specific body language signals and their corresponding meanings. Observe your dog’s behavior and compare it to the chart to gain insights.
Why is it important to understand dog body language?
Understanding body language allows you to communicate effectively with your dog, anticipate their needs, and ensure their well-being.