In the realm of linguistics, the concept of “closest language to English” has captivated scholars and language enthusiasts alike. Understanding the linguistic proximity between languages sheds light on their historical evolution, mutual intelligibility, and cultural interconnectedness. This exploration will delve into the multifaceted factors that determine language closeness, unraveling the linguistic tapestry that binds languages together.
The journey begins with an examination of linguistic similarity, delving into the methods used to quantify the overlap in vocabulary, grammar, and structure between languages. Lexical overlap, the shared vocabulary between languages, plays a crucial role in determining their proximity.
Syntactic structure, the way words are arranged to form sentences, also contributes significantly to language closeness.
Linguistic Similarity
Linguistic similarity refers to the degree to which two languages share similar characteristics in their grammar, vocabulary, and pronunciation. Measuring linguistic similarity is crucial for various linguistic studies, such as language classification, historical linguistics, and computational linguistics.
The measurement of linguistic similarity involves a range of methods, each with its own advantages and limitations. One common approach is lexical similarity, which compares the vocabulary of two languages. Another method is syntactic similarity, which focuses on the structural similarities in sentence construction.
Phonological similarity, on the other hand, examines the sound systems of the languages being compared.
Methods for Calculating Linguistic Similarity
- Lexical similarity:Measures the overlap in vocabulary between two languages. Common metrics include the Levenshtein distance and the Jaccard index.
- Syntactic similarity:Compares the grammatical structures of two languages. Metrics like the Tree Edit Distance and the Dependency Tree Similarity are used for this purpose.
- Phonological similarity:Analyzes the sound systems of two languages. The Levenshtein distance and the Longest Common Subsequence algorithm are often employed for this task.
Lexical Overlap

Lexical overlap refers to the degree to which two languages share the same words or morphemes. It is a key factor in determining the proximity of languages, as it indicates the extent to which they have evolved from a common ancestor or have been in contact with each other.
Measuring lexical overlap is crucial for understanding the relationship between languages. Several approaches are used to quantify this overlap, including the following:
Cognate Counting
Cognate counting involves identifying words in two languages that share a common origin. The number of cognates is then used to calculate the percentage of lexical overlap. This approach is straightforward and provides a reliable measure of the historical relatedness of languages.
Swadesh List Comparison, Closest language to english
The Swadesh list is a set of 200 words that are considered to be basic vocabulary in most languages. By comparing the Swadesh lists of two languages, researchers can determine the number of words that are shared. This approach is useful for comparing languages that may not have a close historical relationship.
Lexical Similarity Metrics
Lexical similarity metrics use statistical techniques to measure the degree of overlap between two languages. These metrics consider factors such as word frequency, semantic similarity, and morphological complexity. They provide a more nuanced measure of lexical overlap than simple cognate counting.
Lexical overlap can vary significantly across languages. For example, English and French share a high degree of lexical overlap due to their shared Romance ancestry. In contrast, English and Japanese have a relatively low degree of lexical overlap, reflecting their distinct linguistic histories.
Syntactic Structure

Syntactic structure plays a pivotal role in determining language proximity. It refers to the arrangement and relationship of words within a sentence, providing a framework for expressing meaning.
Syntactic analysis, used to compare languages, operates at different levels:
Word Order
- The order of subject, verb, and object within a sentence can vary across languages.
- Languages with similar word order patterns tend to be more closely related.
Phrase Structure
- Phrases are groups of words that function as units within a sentence.
- The structure of phrases, such as noun phrases or verb phrases, can reveal similarities between languages.
Sentence Structure
- Sentences can be classified based on their complexity and the number of clauses they contain.
- Languages that share similar sentence structures are likely to be more closely related.
Syntactic similarity can provide strong evidence of language closeness. For example, English and German share many syntactic features, such as the use of subject-verb-object word order and similar phrase structures. This syntactic affinity suggests a close historical relationship between these languages.
Historical Evolution
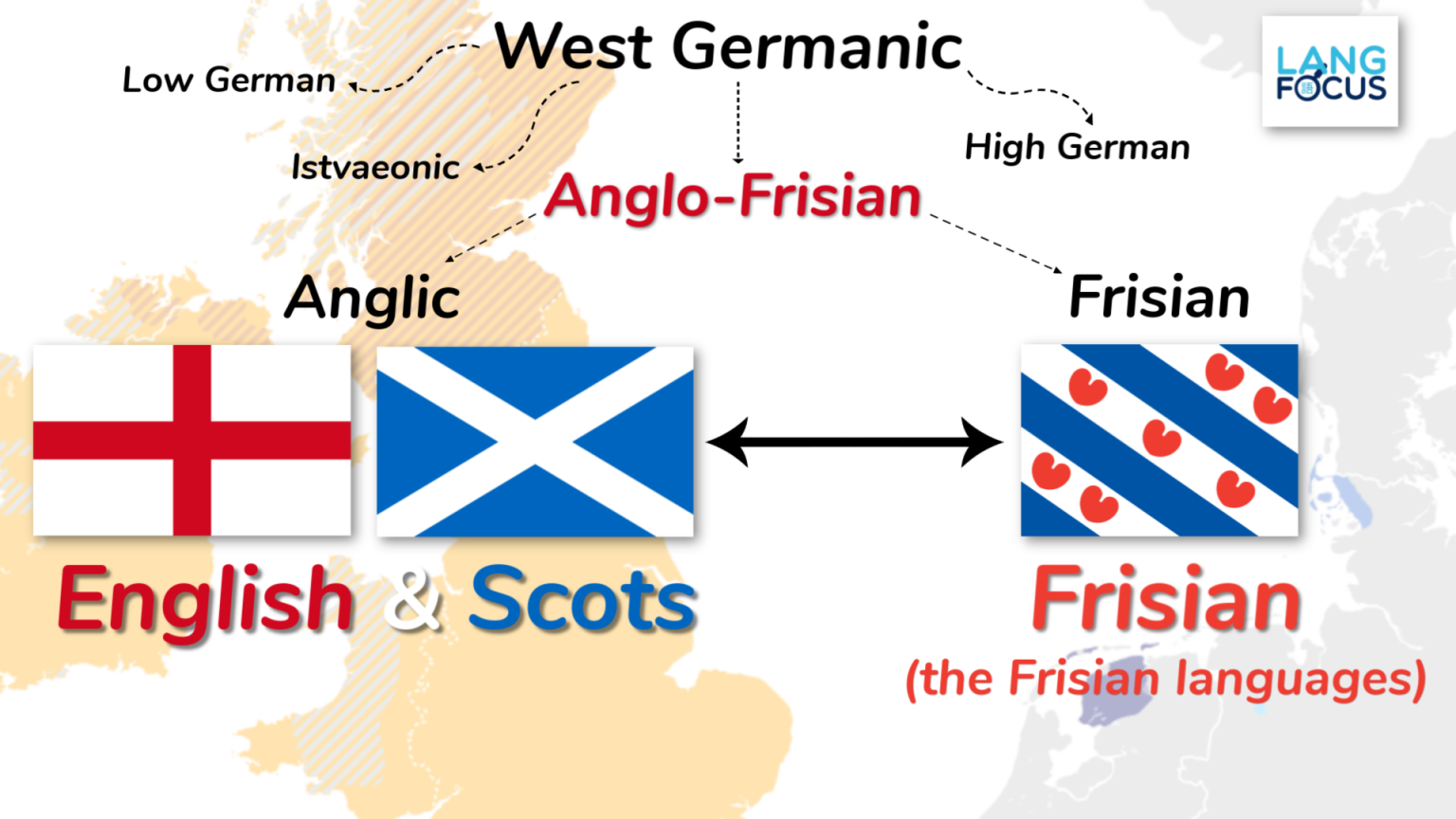
Historical evolution plays a pivotal role in shaping language proximity. Shared ancestry and language contact are two key factors that influence the similarity between languages.
Languages that share a common ancestor, known as a proto-language, tend to exhibit significant similarities in their vocabulary, grammar, and pronunciation. This is because they have inherited these features from their shared ancestor.
Language Families
Languages that share a common ancestor are grouped into language families. Some of the major language families include:
- Indo-European
- Sino-Tibetan
- Afro-Asiatic
- Austronesian
- Niger-Congo
Within each language family, there are subfamilies and branches that represent different stages of linguistic evolution.
Language Contact
Language contact occurs when speakers of different languages interact and influence each other’s speech. This can lead to the borrowing of words, phrases, and grammatical structures from one language to another.
For example, English has borrowed many words from French, such as “cuisine,” “rendezvous,” and “ballet.”
Language contact can also lead to the development of pidgins and creoles, which are simplified languages that emerge from the interaction of two or more languages.
Mutual Intelligibility
Mutual intelligibility refers to the ability of speakers of different languages to understand each other without requiring an intermediary language or translation. It is a crucial factor in determining the proximity of languages and plays a significant role in facilitating communication and cultural exchange.
Factors Contributing to Mutual Intelligibility
- Lexical Similarity:The degree to which two languages share common vocabulary and words with similar meanings.
- Syntactic Similarity:The extent to which the languages share similar grammatical structures and word order patterns.
- Phonological Similarity:The degree to which the sound systems of the languages are similar, allowing for easier recognition and pronunciation.
- Cultural Proximity:The extent to which the speakers of the languages share cultural and historical backgrounds, which can influence language usage and comprehension.
- Exposure and Language Contact:The frequency and duration of contact between speakers of the languages, which can promote mutual intelligibility over time.
Examples of Mutual Intelligibility
The degree of mutual intelligibility between languages can vary greatly. Here are a few examples:
- High Mutual Intelligibility:Languages within the same language family, such as Spanish and Portuguese, or Norwegian and Swedish, often have a high degree of mutual intelligibility due to shared linguistic features.
- Partial Mutual Intelligibility:Languages that share some linguistic similarities but also have significant differences, such as Hindi and Urdu, or English and Dutch, may have partial mutual intelligibility, allowing for some degree of understanding.
- Low Mutual Intelligibility:Languages from different language families, such as English and Chinese, or Arabic and French, typically have very low mutual intelligibility, requiring significant effort and language learning for effective communication.
Last Word: Closest Language To English
The exploration of language proximity culminates in a deeper understanding of the historical forces that have shaped languages. Shared ancestry and language contact have left indelible marks on linguistic landscapes, influencing the evolution of languages and their mutual intelligibility. Mutual intelligibility, the ability of speakers of different languages to understand each other, serves as a testament to the interconnectedness of languages and the power of human communication.
General Inquiries
What factors determine the closest language to English?
Linguistic similarity, lexical overlap, syntactic structure, historical evolution, and mutual intelligibility are key factors that influence the proximity between languages.
How is lexical overlap measured?
Lexical overlap can be measured using various methods, such as the Levenshtein distance, which calculates the number of edits required to transform one word into another.
What role does historical evolution play in language proximity?
Shared ancestry and language contact can significantly influence language proximity. Languages that share a common ancestor tend to exhibit greater linguistic similarity.