Believe in spanish language – Belief is an integral aspect of Spanish culture, shaping its traditions, customs, and language. From the influence of religion to the importance of family and community, belief permeates Spanish society and finds expression in the Spanish language itself. This article delves into the fascinating relationship between belief and the Spanish language, exploring how beliefs are conveyed through grammar, syntax, and common phrases and idioms.
Through examples and analysis, we will uncover the role of belief in shaping Spanish literature, art, and architecture, revealing the profound impact it has had on Spanish culture and identity.
Belief in Spanish Culture
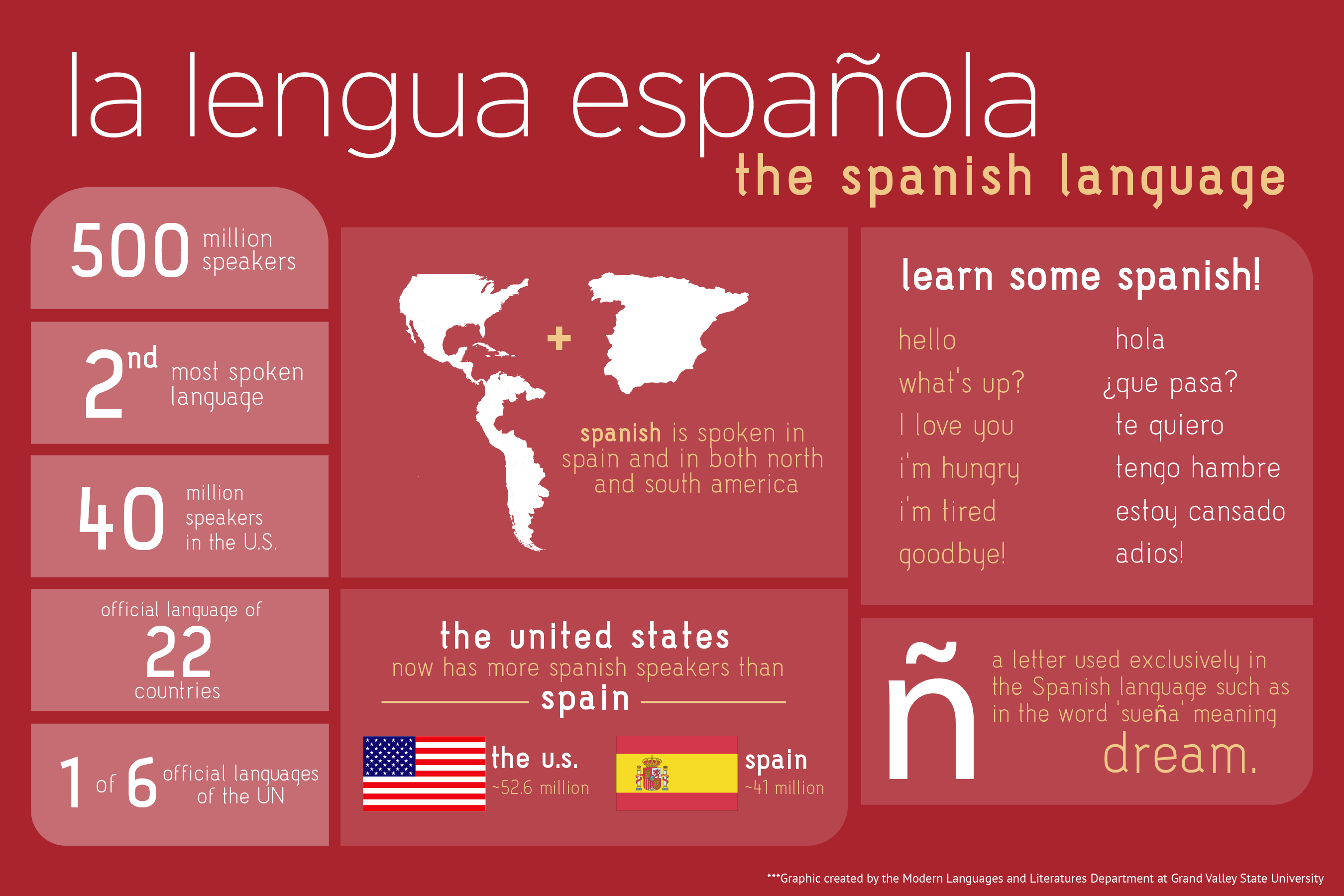
Beliefs and values have played a significant role in shaping the cultural identity of Spain throughout history. From ancient traditions to modern customs, religious influences to societal norms, the Spanish people’s beliefs have left an enduring mark on their culture.
Historical Significance
The history of Spain is deeply intertwined with the beliefs of its people. The country’s early inhabitants, the Celts and Iberians, held animistic beliefs that attributed spiritual powers to natural phenomena. With the arrival of Christianity in the 1st century AD, Spain became a predominantly Catholic nation, and the influence of the Church played a crucial role in shaping Spanish society for centuries.
Influence on Traditions and Customs
Spanish beliefs have profoundly influenced the country’s traditions and customs. For example, the importance of family and community is deeply rooted in Spanish culture, reflecting the Catholic emphasis on love and charity. Religious festivals and celebrations, such as Semana Santa (Holy Week) and the Feast of San Fermín, are integral parts of Spanish life.
Role of Religion
Religion has been a dominant force in shaping Spanish beliefs and values. Catholicism has provided a moral framework for society, influencing everything from personal ethics to political institutions. The Church has also played a significant role in education, healthcare, and social welfare in Spain.
Common Spanish Beliefs and Values

Spanish culture is deeply rooted in a set of core beliefs and values that shape the way people live, interact, and perceive the world. These beliefs have been passed down through generations and continue to play a significant role in shaping Spanish society today.
One of the most fundamental beliefs held by Spanish people is the importance of family. Family is considered the cornerstone of society, and strong family ties are highly valued. Extended families often live close together and maintain close relationships. Respect for elders is also deeply ingrained in Spanish culture, and children are taught to honor and obey their parents and grandparents.
Another important value in Spanish culture is community. Spaniards are proud of their local communities and take an active role in community affairs. They are willing to help their neighbors and support local businesses. Community festivals and events are common and provide opportunities for people to come together and celebrate their shared heritage.
Respect is another core value in Spanish culture. Spaniards are taught to be respectful of others, regardless of their age, gender, or social status. Politeness and good manners are highly valued, and people are expected to treat each other with dignity and courtesy.
Spanish beliefs and values are similar to those of other cultures in many ways. For example, the importance of family and community is shared by many cultures around the world. However, there are also some unique aspects of Spanish culture that set it apart from others.
One of the most distinctive aspects of Spanish culture is its emphasis on personalismo. Personalismo is a belief that relationships are more important than rules or institutions. Spaniards are more likely to trust their personal relationships than they are to rely on impersonal rules or systems.
Another unique aspect of Spanish culture is its emphasis on fatalism. Fatalism is the belief that events are predetermined and that there is little that people can do to change their fate. Spaniards are often resigned to the idea that things will happen as they are meant to happen, and they are less likely to try to control their circumstances than people from some other cultures.
The beliefs and values of Spanish people have a profound impact on their daily lives. They shape the way they interact with each other, the way they raise their children, and the way they view the world. Understanding these beliefs and values is essential for understanding Spanish culture.
Expression of Belief in Spanish Language
Belief in Spanish culture encompasses a complex tapestry of religious, cultural, and personal convictions. The Spanish language itself serves as a rich medium through which these beliefs are expressed, reflecting the deep-seated values and traditions of the Spanish-speaking world.
Spanish grammar and syntax play a significant role in shaping the expression of belief. The use of the subjunctive mood, for example, conveys uncertainty or possibility, often employed to express beliefs or opinions. Additionally, the use of modal verbs, such as “creer” (to believe) and “pensar” (to think), helps to indicate the speaker’s level of conviction.
Common Spanish Phrases and Idioms Reflecting Beliefs
The Spanish language is replete with common phrases and idioms that encapsulate deeply held beliefs and values. These expressions provide insights into the cultural psyche and the ways in which Spaniards perceive the world around them.
| Phrase | Meaning | Implied Belief |
|---|---|---|
| “El que no arriesga, no gana.” | “He who does not risk, does not win.” | Belief in the importance of taking risks to achieve success |
| “No hay mal que por bien no venga.” | “There is no evil that does not come for good.” | Belief in the ultimate goodness of life and the ability to find silver linings in adversity |
| “Más vale pájaro en mano que ciento volando.” | “A bird in the hand is worth more than a hundred flying.” | Belief in the value of certainty and practicality over potential gains |
Belief in Spanish Literature: Believe In Spanish Language
Belief plays a pivotal role in shaping Spanish literature, from the classic works of Cervantes to contemporary novels. Literary characters often embody or challenge Spanish beliefs, and the themes and narratives of Spanish literature are deeply influenced by the beliefs of its authors and readers.
Classic Spanish Literature
In classic Spanish literature, belief is often central to the protagonist’s journey. For example, in Miguel de Cervantes’s “Don Quixote,” the titular character’s belief in the ideals of chivalry leads him on a series of misadventures. Similarly, in Lope de Vega’s “Fuenteovejuna,” the villagers’ belief in their collective power allows them to resist oppression.
Contemporary Spanish Literature
In contemporary Spanish literature, belief continues to be a major theme. For example, in Javier Marías’s “Your Face Tomorrow,” the protagonist’s belief in the power of storytelling shapes his experiences. Similarly, in Elena Ferrante’s “My Brilliant Friend,” the protagonist’s belief in her own strength and resilience allows her to overcome adversity.
Belief and the Themes of Spanish Literature
Belief has also shaped the themes of Spanish literature. For example, the theme of honor is central to many Spanish works, reflecting the importance of belief in one’s own worth and the importance of social status. Similarly, the theme of love is often explored in Spanish literature, reflecting the belief in the power of love to overcome obstacles.
Belief in Spanish Art and Architecture

Belief has profoundly influenced Spanish art and architecture, shaping its aesthetics, themes, and symbolism. From grand cathedrals to intricate paintings, Spanish artistic expressions have served as a testament to the deep-rooted faith and cultural beliefs of the Spanish people.
Religious Iconography and Symbolism, Believe in spanish language
Spanish art is replete with religious iconography and symbolism. The depiction of biblical figures, saints, and religious symbols is a prominent feature, reflecting the Catholic faith’s central role in Spanish society. These symbols often convey specific meanings and messages, such as the Virgin Mary representing purity and grace, or the cross symbolizing sacrifice and redemption.
Architectural Grandeur and Spirituality
Spanish architecture is renowned for its grandeur and spirituality. Cathedrals and churches, such as the Sagrada Familia in Barcelona and the Seville Cathedral, are architectural masterpieces that showcase the fusion of religious beliefs and artistic ingenuity. Their soaring spires, intricate facades, and opulent interiors create an awe-inspiring atmosphere that invites contemplation and worship.
The Influence of Moorish Art
The influence of Moorish art is evident in Spanish architecture, particularly in the southern region of Andalusia. The Alhambra Palace in Granada, a UNESCO World Heritage Site, is a prime example of this fusion. Its intricate geometric patterns, horseshoe arches, and opulent decorations reflect the artistic traditions of the Islamic world, blending seamlessly with Spanish architectural styles.
Contemporary Expressions of Belief
In contemporary times, Spanish art continues to reflect the influence of belief, albeit in more subtle and abstract ways. Artists such as Salvador Dalí and Antoni Tàpies have explored religious and spiritual themes through their works, often using symbolism and surrealist techniques to convey their beliefs and ideas.
Ultimate Conclusion
The exploration of belief in the Spanish language unveils a rich tapestry of cultural and linguistic connections. It showcases how language not only reflects beliefs but also shapes and perpetuates them. By understanding the expression of belief in Spanish, we gain insights into the heart of Spanish culture and its enduring legacy.
FAQ Guide
What is the significance of belief in Spanish culture?
Belief plays a central role in Spanish culture, influencing traditions, customs, and values. It has been shaped by historical events, religious influences, and social norms, and continues to shape Spanish society.
How is belief expressed in the Spanish language?
Belief is expressed in the Spanish language through grammar, syntax, and common phrases and idioms. For example, the use of the subjunctive mood conveys uncertainty or belief, while certain idioms reflect cultural beliefs about family, respect, and religion.
What role does belief play in Spanish literature?
Belief is a major theme in Spanish literature, from classic works to contemporary novels. Literary characters often embody or challenge Spanish beliefs, and the exploration of belief shapes the themes and narratives of many Spanish literary works.